Best Dialysis Diet Tips for Better Kidney Health
Managing a dialysis patient diet is crucial for maintaining kidney health and overall well-being. The challenges of following a restrictive diet can be overwhelming, but making informed food choices can significantly improve your quality of life. Chronic kidney disease affects approximately 800 million people worldwide, with millions relying on dialysis to survive 1. Proper dietary management, including controlling intake of sodium, potassium, and phosphorus, plays a key role in supporting kidney function and reducing complications.
In this blog, we will explore essential dietary tips and foods that are vital for dialysis patients to maintain optimal health.
Key Takeaways:
- Managing sodium, potassium, and phosphorus intake is critical for dialysis patients to support kidney health.
- A balanced dialysis patient diet, including lean proteins and low-potassium vegetables, can significantly improve overall health and dialysis outcomes.
- Proper fluid control is crucial for dialysis patients, as excessive fluid intake can lead to serious heart and kidney complications.

Core Nutritional Considerations for Dialysis Patients
A dialysis patient’s diet requires limiting fluid intake, as well as sodium, potassium, and phosphorus, while maintaining a healthy diet.
- Protein Intake Management: One of the critical elements to consider for a dialysis patient diet is the average protein intake. It is essential to select foods such as lean meats, poultry, fish, and eggs that help manage waste products from protein breakdown.
- Potassium Level Control: Avoid foods high in potassium, such as tomatoes, oranges, and dried fruits. If you are someone suffering from excruciating kidney disease, it is essential to regulate potassium levels, as it accumulates easily to unsafe levels.
- Phosphorus Regulation: You must reduce the intake of food with high levels of phosphorus, such as milk, cheese, nuts, and more, to safeguard bones and blood vessels. Higher levels of phosphorus tend to weaken blood vessels and damage bones.
- Restriction on Sodium Intake: It is critical to avoid salty foods, to control blood pressure and reduce fluid retention. Moreover, patients on dialysis should limit their daily fluid intake.
Now, let’s explore some typical food for dialysis patients that help maintain stable renal health.
Typical foods for kidney patients
For a dialysis patient diet, selecting appropriate foods is essential to manage potassium, phosphorus, and sodium levels. Appropriately focusing on nutrient-dense, low-sodium options, you can help support kidney function and improve dialysis outcomes.
Here are some of the food for dialysis patient which are critical for a better lifestyle:
- Cauliflower is one of the most common foods, rich in several nutrients, including Vitamins K, C, and B, and has anti-inflammatory properties. Recommended servings include 124 grams of cooked cauliflower, which provides 19mg, 40mg, and 176mg of sodium, phosphorus, and potassium, respectively.
- Egg whites are a rich source of high-quality proteins and therefore make for a good renal-friendly food. Egg whites of 66 grams contain 110 mg, 108 mg, and 10 mg of sodium, potassium, and phosphorus.
- Garlic is a possible alternative to salt, as salt intake is restricted for patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Garlic has vitamin C, manganese, and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Pineapple is a great fruit choice for kidney diets due to its low potassium levels. In addition, it is a good source of bromelain, manganese, and vitamin C. A 165-gram pineapple includes 2mg, 180mg and 16mg of sodium, potassium, and phosphorus.
Now, let’s understand the dialysis patient diet chart, which is critical for appropriate kidney function.
Role of Fluids and Salt Control in the Dialysis Patient’s Diet
When following a dialysis patient diet, controlling fluids and salt intake is central. Too much salt or fluid can cause your body to retain water, raise blood pressure, and increase the burden on your heart and dialysis treatment.
Here are some of the considerations for controlling salt and fluid control for dialysis patients:
- Sodium (salt) limit: Aim for less than 2.0 g sodium per day (5 g salt) or at most 2.3 g sodium ( 5–6 g salt) per day 2.
- Daily fluid intake: Many dialysis patients are advised to restrict fluid intake to about 32 ounces (1 litre)daily, unless urine output allows slightly more.
- Inter‑dialysis weight gain: Try to keep fluid weight gain between dialysis sessions below 1.5–2.0 kg (3–4 lb) to avoid fluid overload.
- Avoid hidden sodium & fluids: Many processed foods, canned goods, sauces, and soups contain high levels of sodium or fluids; check labels carefully and choose fresh, unprocessed foods.
- Track fluid from all sources: Fluids include not just drinks, but also soups, ice cream, gelatin, water in cooked foods, and even moisture from certain fruits or vegetables.
To support kidney health, here’s a detailed diet plan for dialysis patient.
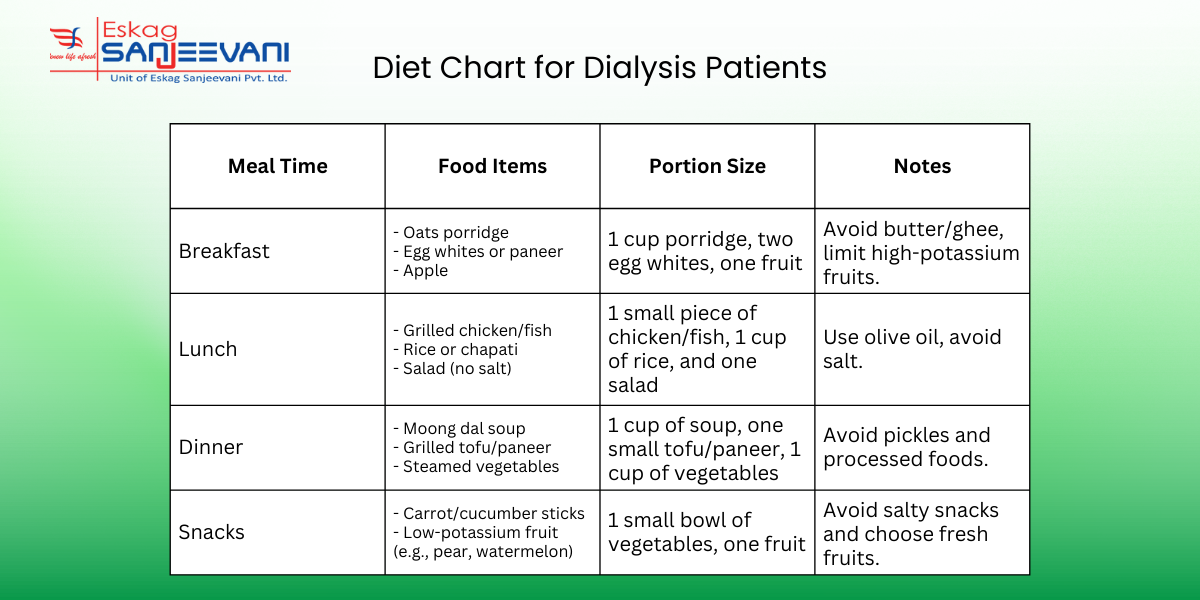
Diet Chart for Kidney Patients
A well-structured diet plan is critical for dialysis patients to maintain their health and manage kidney function. You can control your nutrient intake and avoid complications such as fluid retention and high potassium levels by making appropriate food choices.
Here’s a comprehensive overview of a dialysis patient diet chart:
- Breakfast: Start the day with a low-potassium fruit such as apples or berries, paired with egg whites or whole-grain toast. Avoid high-sodium spreads like butter or jam.
- Lunch: Choose a lean protein, such as grilled chicken, paired with a portion of low-potassium vegetables, such as cauliflower or bell peppers. Avoid high-sodium soups or processed meats.
- Dinner: Important to go for a small portion of fish, with rice and a salad. Steer clear of processed sauces or dressings.
- Snacks: Healthy options include a handful of grapes. It is also essential to avoid salty snacks such as chips.
- Hydration: Keep fluid intake in check, limiting coffee or juice to the recommended amounts.
Also read: Types of Dialysis: Exploring Options for Kidney Failure Treatment.
Final Thoughts
Maintaining a proper diet is vital for dialysis patients to manage kidney function and improve overall health. Being cautious of sodium, potassium, and phosphorus intake and staying on top of fluid limits, you can prevent kidney complications. Adopting healthy eating habits and reading food labels can significantly improve your dialysis patient’s diet and long-term health.
At Eskag Sanjeevani Dialysis, the focus is not only on providing top-quality dialysis services but also on offering comprehensive care tailored to your specific needs. Their expert team ensures that your diet and treatment plan align for the best possible results. By maintaining open communication with your healthcare team at Eskag Sanjeevani, you can take a proactive approach to managing your kidney health and improving your quality of life.
References
Dialysis patients should focus on lean proteins like chicken, fish, and egg whites, along with low-potassium vegetables. Avoid high-phosphorus foods like dairy, processed meats, and canned items.
Dialysis patients must monitor fluid intake and stick to the recommended limit set by their healthcare provider. Limiting high-fluid foods like soups and watery fruits can help manage daily fluid intake.
Yes, sodium intake should be restricted to prevent fluid retention, which increases blood pressure and strains the kidneys. Use of spices instead of salt is an effective way to lower sodium intake.
Dialysis patients can eat fruits, but should avoid high-potassium options like bananas, oranges, and avocados. Safe choices include apples, berries, and grapes, which are lower in potassium.
Protein intake is essential for dialysis patients, as they need more to maintain muscle mass and strength. Lean meats, fish, and egg whites provide high-quality protein without excess phosphorus.

